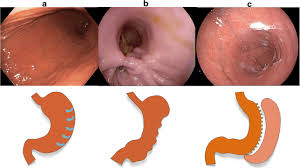
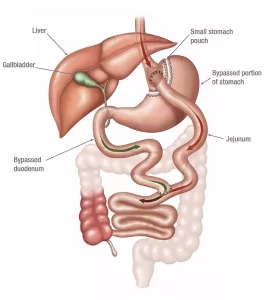
Gastric Bypass Surgery
Table of Contents
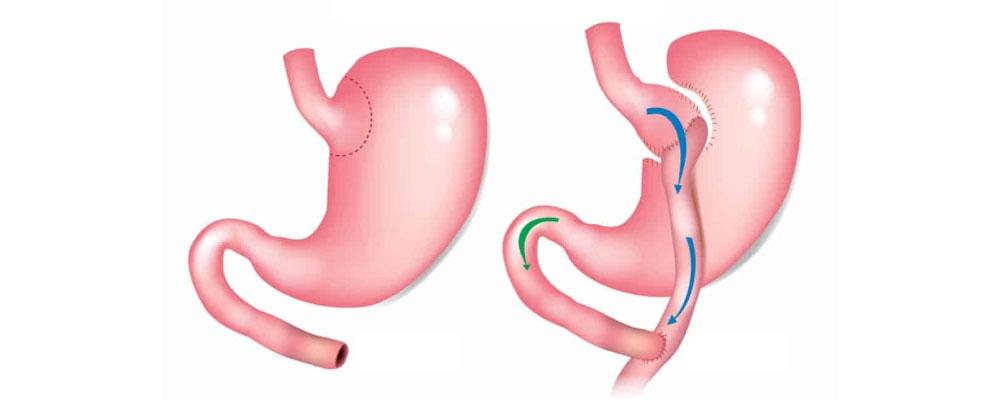
Introduction to Gastric Bypass Surgery
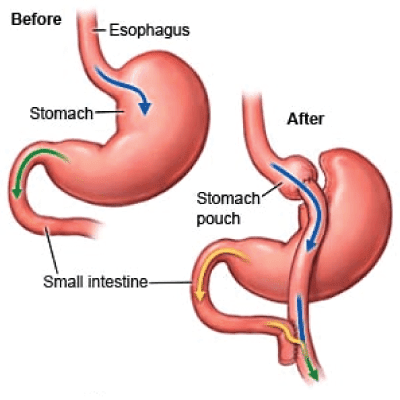
Gastric bypass surgery is a type of weight loss surgery that alters the digestive system to limit the amount of food a person can eat and absorb. During the procedure, the surgeon creates a small pouch at the top of the stomach and attaches it to the small intestine, bypassing a portion of the stomach and intestine. This reduces the amount of food that can be eaten at one time and decreases the absorption of calories and nutrients. The procedure can be performed using open surgery or minimally invasive techniques such as laparoscopy.
Who is Eligible for Gastric Bypass Surgery?
Gastric bypass surgery is typically recommended for people who have a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or higher, or a BMI of 35 or higher with one or more obesity-related health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, or sleep apnea. Candidates for the surgery should also have attempted to lose weight through diet and exercise without success. It is important for patients to understand that gastric bypass surgery is not a quick fix or an easy way out, and requires a lifelong commitment to lifestyle changes.
Benefits and Risks of Gastric Bypass Surgery
The benefits of gastric bypass surgery can be significant for those struggling with obesity and related health complications. Studies have shown that patients who undergo gastric bypass surgery can lose an average of 60-80% of their excess weight within the first year, and many experience improvements in their overall health and quality of life[8]. These improvements can include resolution or improvement of type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, and other obesity-related conditions.
However, like any surgical procedure, gastric bypass surgery carries risks. These can include bleeding, infection, blood clots, and complications related to anesthesia. There is also a risk of long-term complications such as malnutrition, dumping syndrome (a condition where food moves too quickly through the digestive system), and hernias. Patients should carefully weigh the potential benefits and risks of the procedure with their healthcare provider before making a decision.
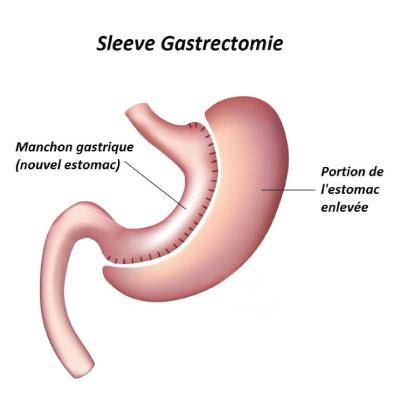
Different Types of Gastric Bypass Surgery
There are several different types of gastric bypass surgery, each with its own benefits and risks. The most common type is Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, which involves creating a small pouch at the top of the stomach and attaching it to a section of the small intestine. This bypasses the rest of the stomach and the duodenum, the first part of the small intestine. Another type is the biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch, which removes a larger portion of the stomach and reroutes the small intestine in a more complex manner. This procedure is typically reserved for patients with a higher BMI or more severe health complications.
Preparing for Gastric Bypass Surgery
Preparing for gastric bypass surgery involves making significant lifestyle changes in the months leading up to the procedure. This can include following a specific diet, losing weight, quitting smoking, and increasing physical activity. Patients will also need to undergo a thorough medical evaluation to ensure they are healthy enough for surgery and to identify any potential risks or complications.
What to Expect During Gastric Bypass Surgery
Gastric bypass surgery typically takes 2-3 hours and is performed under general anesthesia. During the procedure, the surgeon will make several small incisions in the abdomen and use specialized instruments to create the new stomach pouch and reroute the small intestine. Patients will be closely monitored during the surgery and will typically spend 1-2 nights in the hospital for recovery.

Recovery and Post-Operative Care
Recovery from gastric bypass surgery can be a challenging process, and patients will need to follow strict guidelines to ensure proper healing and prevent complications. This can include taking pain medication, following a liquid diet for several weeks, gradually reintroducing solid foods, and participating in regular exercise. Patients will also need to attend follow-up appointments with their healthcare provider to monitor their progress and make adjustments to their diet and medication as needed.
Diet and Nutrition After Gastric Bypass Surgery
Diet and nutrition are critical components of a successful gastric bypass surgery outcome. Patients will need to follow a strict diet plan that gradually reintroduces solid foods and emphasizes protein, fiber, and nutrient-dense foods. They will also need to take vitamin and mineral supplements for the rest of their lives to prevent malnutrition. Patients should work closely with a registered dietitian to develop a personalized nutrition plan that meets their individual needs and goals.
Long-Term Effects and Outcomes of Gastric Bypass Surgery
The long-term effects of gastric bypass surgery can be significant for patients who are able to successfully maintain their weight loss and make lifestyle changes. Studies have shown that patients who undergo the procedure can experience improvements in overall health and quality of life, as well as a reduced risk of obesity-related health complications. However, it is important to note that weight regain can occur if patients do not continue to follow a healthy diet and exercise routine.
Alternative Weight Loss Options
Gastric bypass surgery is not the only option for weight loss, and patients should carefully consider all options before making a decision. Other options can include lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise, medication, and other surgical procedures such as gastric sleeve or adjustable gastric banding. Patients should work closely with their healthcare provider to develop a personalized weight loss plan that meets their individual needs and goals.