Behavioral therapy: comprehensive guide to molding minds
Table of Contents

Introduction
Behavioral therapy is a powerful approach that holds the potential to reshape lives and foster positive change. By understanding the principles and techniques of behavioral therapy, individuals can gain invaluable insights into their own behaviors and develop strategies to overcome challenges, improve mental health, and enhance overall well-being.
This comprehensive guide to behavioral therapy, we will explore the foundations, applications, and benefits of this evidence-based therapeutic approach. Drawing upon the principles of behavior analysis, assessment, and modification, behavioral therapy offers a structured and goal-oriented framework for addressing a wide range of psychological and behavioral issues.
Key concepts and techniques of behavioral therapy
Role of the therapist in behavioral therapy
Key concepts and techniques of behavioral therapy, including behavior analysis, goal-setting, reinforcement, and behavior modification strategies. Examining real-life examples and success stories, we will illustrate the effectiveness of behavioral therapy in diverse contexts, such as children and adolescents, mental health disorders, and addiction.
Examining their qualifications, therapeutic techniques, and the collaborative nature of the therapist-client relationship. The ethical considerations and guidelines that govern the practice of behavioral therapy will also be discussed, emphasizing the importance of confidentiality, informed consent, and cultural competence.
By the end of this guide, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of behavioral therapy, its applications, and its potential to bring about positive transformation. With this knowledge, individuals can navigate their own paths to personal growth, resilience, and a life marked by positive change.
Understanding behavioral therapy
Behavioral therapy is a psychological approach that focuses on modifying and altering behaviors to promote positive change in individuals. It is based on the principles of behaviorism, which emphasize the influence of the environment on behavior and the idea that behaviors can be learned, unlearned, and modified through conditioning [4]. This therapeutic approach aims to identify and target specific behaviors that contribute to psychological distress or maladaptive patterns.
The foundation of behavioral therapy lies in behavior analysis and assessment. Therapists utilize various assessment tools and techniques to gather data on the client’s behaviors, their antecedents (triggers), and the consequences that reinforce or discourage those behaviors. This analysis helps identify the function and purpose of the behavior, allowing therapists to develop appropriate intervention strategies [5].
Setting clear and achievable goals is another crucial aspect of behavioral therapy.
By collaborating with the client, therapists establish specific and measurable objectives that define the desired behavioral changes. These goals provide a framework for therapy sessions and guide the implementation of behavior modification techniques.
Reinforcement and punishment are key components of behavioral therapy. Positive reinforcement involves providing rewards or incentives to reinforce desired behaviors, while punishment involves applying consequences to discourage undesirable behaviors. These techniques help individuals acquire new behaviors or eliminate problematic ones [6].
Functional analysis
Functional analysis is employed to understand the underlying causes and maintaining factors of behaviors. By examining the antecedents, consequences, and contextual factors associated with a behavior, therapists gain insights into the function it serves for the individual. This understanding allows for tailored interventions that address the root causes of the behavior [7].
Behavior modification techniques are utilized to promote behavior change. These techniques include operant conditioning, where behaviors are shaped through reinforcement and punishment, as well as systematic desensitization, which helps individuals overcome phobias and anxieties through gradual exposure and relaxation techniques. Cognitive-behavioral techniques, such as cognitive restructuring, are also integrated to address maladaptive thoughts and beliefs that influence behavior [8].
The principles and techniques of behavioral therapy provides individuals with a comprehensive approach to tackle a wide range of behavioral issues, including anxiety disorders, depression, addiction, and more. By addressing behaviors and modifying them in a structured and evidence-based manner, behavioral therapy empowers individuals to make positive changes and improve their overall well-being.
Common applications of behavioral therapy
Behavioral therapy has proven to be highly effective in addressing a wide range of psychological and behavioral issues across various populations. By targeting specific behaviors and modifying them through evidence-based techniques, behavioral therapy has demonstrated success in several areas.
In children and adolescents, behavioral therapy has shown promising results in managing attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Techniques such as token economies, where desirable behaviors are rewarded, and behavior contracts, which establish clear expectations and consequences, have been effective in improving attention, impulse control, and academic performance [9].
Behavioral therapy for oppositional defiant disorder and autism spectrum disorder
Oppositional defiant disorder (ODD) is another condition that can benefit from behavioral therapy interventions. By using techniques like parent management training, therapists help parents implement consistent discipline strategies, improve communication, and teach problem-solving skills, thereby reducing defiant behaviors and improving family functioning [10].
Behavioral therapy has also proven valuable in supporting individuals on the autism spectrum. Applied behavior analysis (ABA) is a well-established and evidence-based approach that focuses on teaching new skills and reducing problematic behaviors. ABA utilizes techniques such as discrete trial training, reinforcement schedules, and visual supports to promote communication, social skills, and adaptive behaviors in individuals with autism [11].
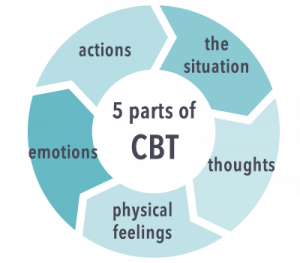
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
In the realm of mental health, behavioral therapy has been effective in addressing anxiety disorders. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), a form of behavioral therapy, helps individuals identify and challenge irrational thoughts and beliefs that contribute to anxiety. Through exposure therapy and relaxation techniques, individuals learn to confront feared situations and develop effective coping strategies [12].
Struggling with substance abuse and addiction, behavioral therapy approaches such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and contingency management have been successful in promoting abstinence and preventing relapse. These approaches focus on identifying triggers, developing coping skills, and reinforcing positive behaviors through incentives [13].
Practical and evidence-based strategies to address a variety of psychological and behavioral issues in different populations. By tailoring interventions to specific conditions and individual needs, behavioral therapy empowers individuals to make positive changes and achieve improved mental health and well-being.
The role of the therapist in behavioral therapy
The therapist plays a vital role in the effective implementation of behavioral therapy techniques and in guiding individuals towards positive behavior change. With their expertise and training, therapists create a supportive and collaborative environment for clients to address their behavioral issues.
Therapist qualifications and training are crucial for the successful delivery of behavioral therapy. Professionals in this field often hold advanced degrees in psychology or counseling and receive specialized training in behavioral interventions. They are well-versed in the principles and techniques of behavior analysis, functional assessment, and behavior modification, enabling them to tailor interventions to individual needs [14].
Therapeutic techniques and approaches in behavioral therapy
Therapeutic techniques and approaches employed by behavioral therapists may vary depending on the client’s specific needs and goals. They may use a combination of strategies, including individual therapy, group therapy, or family therapy, depending on the nature of the issue and the context in which the behavior occurs. Therapists also collaborate with other healthcare providers, such as psychiatrists or primary care physicians, to ensure comprehensive care [15].
The therapist-client relationship in behavioral therapy is characterized by collaboration and trust. Therapists actively listen to their clients, provide empathy, and create a non-judgmental space where clients feel safe to explore their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Through a collaborative approach, therapists work together with clients to set goals, identify target behaviors, and develop strategies for behavior change.
The Iterative Process
Moreover, therapists continuously monitor and assess the progress of clients throughout the therapy process. They track behavior changes, adjust interventions as needed, and provide ongoing feedback and support. This iterative process allows therapists to adapt the treatment plan to the individual’s evolving needs and circumstances.
Assuming the role of a guide and facilitator, therapists empower individuals to take ownership of their behavior change journey. They equip clients with the necessary skills and strategies to modify behaviors, cope with challenges, and maintain progress even after therapy concludes.
The therapist’s role in behavioral therapy is multifaceted. They bring expertise, training, and a supportive presence to the therapeutic relationship. Through their guidance, therapists facilitate behavior change, empower individuals, and foster long-lasting positive outcomes.
Effectiveness and benefits of behavioral therapy
Behavioral therapy has demonstrated effectiveness in improving a wide range of psychological and behavioral issues, making it a valuable therapeutic approach. The evidence supporting the efficacy of behavioral therapy is robust, and numerous studies have highlighted its benefits across different populations.
In treating various mental health disorders. Meta-analyses have demonstrated its efficacy in reducing symptoms of anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and specific phobias [16]. Behavioral therapy interventions, such as exposure therapy and cognitive restructuring, have shown significant and lasting effects in alleviating anxiety symptoms.
Behavioral activation, a core component of behavioral therapy, focuses on increasing engagement in pleasurable and meaningful activities, which has been found to alleviate depressive symptoms [17]. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), a form of behavioral therapy that integrates cognitive restructuring, has also been proven effective in the treatment of depression [18].
Behavioral therapy has also demonstrated success in addressing addictive behaviors.
Cognitive-behavioral approaches, such as relapse prevention strategies and contingency management, have shown effectiveness in reducing substance abuse and preventing relapse [19]. These interventions target the underlying behaviors, thoughts, and environmental triggers associated with addictive behaviors, promoting sustained recovery.
One of the key benefits of behavioral therapy is its emphasis on skill-building and self-management. Through behavioral therapy, individuals learn specific techniques and strategies to modify their behaviors, manage their emotions, and cope with challenges. These acquired skills empower individuals to take an active role in their own treatment and facilitate long-term behavior change [20].
Skill-building and self-management
Behavioral therapy has been found to have long-lasting effects. Studies have shown that the benefits of behavioral therapy can persist even after the therapy has ended, with individuals maintaining improvements in behavior and well-being [21]. The durability of the effects makes behavioral therapy a valuable and sustainable treatment option.
Evidence base and offers significant benefits in the treatment of various psychological and behavioral issues. Its effectiveness in reducing symptoms, promoting behavior change, and empowering individuals to manage their own well-being makes it a valuable therapeutic approach.
Integrating Behavioral Therapy with Other Approaches
Behavioral therapy can be effectively integrated with other therapeutic approaches to enhance treatment outcomes and address the multifaceted nature of psychological and behavioral issues. Combining behavioral therapy with complementary modalities, a comprehensive and tailored treatment plan can be created for individuals.
One commonly integrated approach is cognitive-behavioral therapy
(CBT), which combines cognitive restructuring techniques with behavior modification strategies. CBT focuses not only on modifying behaviors but also on identifying and challenging irrational thoughts and beliefs that contribute to psychological distress [22]. By addressing both cognitive and behavioral factors, CBT offers a holistic approach to treatment.
Dialectical behavior therapy
(DBT) is another approach that incorporates behavioral therapy principles. DBT combines elements of cognitive-behavioral techniques with mindfulness practices and acceptance strategies. It is particularly effective in addressing emotion dysregulation, self-destructive behaviors, and borderline personality disorder [23]. DBT emphasizes skill-building, emotional regulation, and interpersonal effectiveness.
Acceptance and commitment therapy
(ACT) is yet another modality that can be integrated with behavioral therapy. ACT focuses on developing psychological flexibility by encouraging individuals to accept their thoughts and emotions while committing to value-driven actions [24]. ACT uses behavioral techniques to promote behavior change while fostering acceptance and mindfulness.
Integrating behavioral therapy with pharmacotherapy
Integrating behavioral therapy with pharmacotherapy can also be beneficial, especially in the treatment of certain mental health conditions. For instance, combining behavioral therapy with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) has shown effectiveness in treating depression and anxiety disorders [25]. This integrated approach addresses both the underlying neurochemical imbalances and the behavioral factors contributing to the symptoms.
Incorporating family therapy or couples therapy alongside behavioral therapy can be valuable in addressing interpersonal dynamics and improving family functioning. Family members or partners can learn behavioral techniques to support the individual’s behavior change, strengthen communication, and promote healthier relationships [26].
Ethics and considerations in behavioral therapy
Ethical guidelines play a crucial role in guiding the practice of behavioral therapy and ensuring the well-being of clients. Behavioral therapists adhere to a set of ethical principles that govern their professional conduct, ensuring the protection of clients’ rights, privacy, and confidentiality.
Confidentiality is a fundamental ethical consideration in behavioral therapy. Therapists are obligated to maintain the privacy of their clients and safeguard the information disclosed during therapy sessions. They must obtain informed consent from clients, clearly explaining the limits of confidentiality and any circumstances where confidentiality may be breached, such as when there is a risk of harm to the client or others [27].
Cultural considerations and diversity are vital ethical considerations in behavioral therapy. Therapists must be aware of and respect cultural, ethnic, and individual differences. They should strive to provide culturally sensitive and inclusive care, recognizing the impact of cultural factors on behavior and tailoring interventions accordingly. Therapists should also engage in ongoing professional development to enhance their cultural competence [28].
Informed consent
Requirement that ensures clients have a clear understanding of the therapy process, potential risks and benefits, and their rights as clients. Therapists must provide relevant information in a comprehensible manner and obtain voluntary consent from clients before initiating treatment. Informed consent also includes informing clients about alternative treatments or approaches, empowering them to make informed decisions about their care [29].
Behavioral therapists are ethically bound to maintain professional boundaries and avoid conflicts of interest. They should refrain from engaging in dual relationships with clients that could impair objectivity or compromise the therapeutic relationship. Therapists must prioritize the best interests of their clients and maintain professional competence through continuing education and adherence to ethical standards [30].
Upholding these ethical considerations, behavioral therapists ensure the provision of ethical, competent, and client-centered care. These principles safeguard the well-being and rights of clients, promoting trust, transparency, and effectiveness in the therapeutic process.
Conclusion
Behavioral therapy, with its evidence-based principles and techniques, offers a comprehensive guide to understanding and modifying behaviors. Throughout this guide, we have explored the foundations, applications, benefits, and ethical considerations of behavioral therapy. By equipping readers with this knowledge, we aim to empower individuals to embark on a journey of personal growth, resilience, and positive change.
The guide has shed light on the key concepts of behavior analysis, goal-setting, reinforcement, and behavior modification, showcasing their effectiveness in diverse contexts such as children and adolescents, mental health disorders, and addiction. We have emphasized the vital role of therapists in delivering behavioral therapy, highlighting their qualifications, therapeutic techniques, and the importance of ethical guidelines.
The ethical considerations in behavioral therapy, including confidentiality, informed consent, and cultural competence, ensures the provision of ethical and client-centered care. Adhering to these principles, therapists create a safe and supportive environment for individuals to address their behavioral issues and achieve meaningful transformations.
With the knowledge gained from this guide, individuals can harness the power of behavioral therapy to reshape their lives, improve mental health, and enhance overall well-being. Utilizing the strategies and techniques provided, readers can mold their minds, overcome challenges, and pave the way for a brighter future.
References
- Abu Dayyeh BK, Kumar N, Edmundowicz SA, et al. ASGE Bariatric Endoscopy Task Force systematic review and meta-analysis assessing the ASGE PIVI thresholds for adopting endoscopic bariatric therapies. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;82(3):425-438.e5.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26232362/
- Sharaiha RZ, Kumta NA, Saumoy M, et al. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty significantly reduces body mass index and metabolic complications in obese patients. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15(4):504-510.e1.
- Jirapinyo P, Haas AV, Thompson CC. Effect of endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty on blood pressure, glucose metabolism, and cardiovascular indices in patients with obesity and metabolic syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17(7):1305-1312.e2.
- Skinner BF. The behavior of organisms: An experimental analysis. New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts; 1938.https://psycnet.apa.org/record/1939-00056-000
- Kazdin AE. Behavior modification in applied settings (7th ed.). Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Cengage Learning; 2012.
- Cooper JO, Heron TE, Heward WL. Applied behavior analysis (2nd ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education; 2007.
- Carr JE, Nosik MR, LeBlanc LA. Functional analysis. In: Fisher WW, Piazza CC, Roane HS, editors. Handbook of applied behavior analysis. New York, NY: Guilford Press; 2011. p. 65-86.https://www.guilford.com/books/Handbook-of-Applied-Behavior-Analysis/Fisher-Piazza-Roane/9781462543755
- Beck JS. Cognitive behavior therapy: Basics and beyond (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Guilford Press; 2011.
- Fabiano GA, Pelham WE Jr, Coles EK, et al. A meta-analysis of behavioral treatments for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Clin Psychol Rev. 2009;29(2):129-140.
- Eyberg SM, Nelson MM, Boggs SR. Evidence-based psychosocial treatments for children and adolescents with disruptive behavior. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2008;37(1):215-237.
- Smith T. Discrete trial training in the treatment of autism. Focus Autism Other Dev Disabl. 2001;16(2):86-92.
- Butler AC, Chapman JE, Forman EM, Beck AT. The empirical status of cognitive-behavioral therapy: A review of meta-analyses. Clin Psychol Rev. 2006;26(1):17-31.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16199119/
- Dutra L, Stathopoulou G, Basden SL, Leyro TM, Powers MB, Otto MW. A meta-analytic review of psychosocial interventions for substance use disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 2008;165(2):179-187.
- McLeod BD, Weisz JR. The therapy process observational coding system for child psychotherapy strategies scale. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2010;39(3):436-443.
- Lambert MJ, Ogles BM. The efficacy and effectiveness of psychotherapy. In: Lambert MJ, editor. Bergin and Garfield’s handbook of psychotherapy and behavior change (6th ed.). New York, NY: Wiley; 2013. p. 169-218.
- Butler AC, Chapman JE, Forman EM, Beck AT. The empirical status of cognitive-behavioral therapy: A review of meta-analyses. Clin Psychol Rev. 2006;26(1):17-31.
- Cuijpers P, van Straten A, Warmerdam L, Andersson G. Psychological treatment of depression: A meta-analytic database of randomized studies. BMC Psychiatry. 2008;8:36.
- Hollon SD, Thase ME, Markowitz JC. Treatment and prevention of depression. Psychol Sci Public Interest. 2002;3(2):39-77.https://psycnet.apa.org/record/2003-09355-001
- Dutra L, Stathopoulou G, Basden SL, Leyro TM, Powers MB, Otto MW. A meta-analytic review of psychosocial interventions for substance use disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 2008;165(2):179-187.
- Kanter JW, Manos RC, Bowe WM, Baruch DE, Busch AM, Rusch LC. What is behavioral activation? A review of the empirical literature. Clin Psychol Rev. 2010;30(6):608-620.
- Weisz JR, Weiss B, Han SS, Granger DA, Morton T. Effects of psychotherapy with children and adolescents revisited: A meta-analysis of treatment outcome studies. Psychol Bull. 1995;117(3):450-468.
- Beck JS. Cognitive behavior therapy: Basics and beyond (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Guilford Press; 2011.
- Linehan MM. Cognitive-behavioral treatment of borderline personality disorder. New York, NY: Guilford Press; 1993.
- Hayes SC, Strosahl KD, Wilson KG. Acceptance and commitment therapy: The process and practice of mindful change (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Guilford Press; 2011.
- DeRubeis RJ, Hollon SD, Amsterdam JD, et al. Cognitive therapy vs medications in the treatment of moderate to severe depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(4):409-416.
- Pinsof WM, Wynne LC. Toward progress research: Closing the gap between family therapy practice and research. J Marital Fam Ther. 1995;21(4):403-418.
- American Psychological Association. Ethical principles of psychologists and code of conduct. Am Psychol. 2002;57(12):1060-1073.
- Sue DW, Arredondo P, McDavis RJ. Multicultural counseling competencies and standards: A call to the profession. J Couns Dev. 1992;70(4):477-486.
- Fisher CB. Decoding the ethics code: A practical guide for psychologists. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications; 2012.
- Koocher GP, Keith-Spiegel P. Ethics in psychology: Professional standards and cases (4th ed.). New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 2016.