Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty patient guide
Table of Contents
Introduction
Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG) is a minimally invasive weight loss procedure that has gained popularity in recent years as a safe and effective alternative to traditional bariatric surgeries. ESG works by reducing the size of the stomach using an endoscope, which leads to a feeling of fullness[1] and helps patients lose weight. In this patient’s guide to ESG, we will provide a comprehensive overview of the procedure, its benefits, risks, and success rates.
The first section of this guide will introduce ESG and explain how it works. We will also compare ESG with other weight loss surgeries and discuss eligibility criteria for ESG. Next, we will discuss how to prepare for ESG, including pre-procedure requirements and dietary and lifestyle changes. We will also provide a detailed description of what to expect during the procedure, the duration of the procedure, and anesthesia during the procedure.
Post-procedure care of endoscopic
After the ESG procedure, patients must follow certain guidelines for post-procedure care and attend follow-up appointments. We will provide an overview of these guidelines and discuss possible side effects.[2] Additionally, we will examine the potential benefits of ESG and possible risks and complications. Finally, we will present an overview of studies and data on ESG’s success rate, including the factors that can affect it.
If you are considering ESG for weight loss, it is essential to understand the procedure fully and to consult with a healthcare provider to determine if it is the right option for you.
Understanding ESG
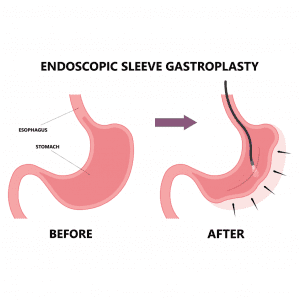
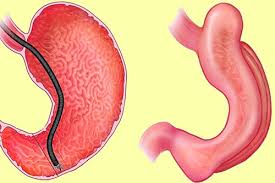
Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG)[3] is a minimally invasive weight loss procedure that involves reducing the size of the stomach using an endoscope. This procedure creates a sleeve-shaped stomach, leading to a feeling of fullness and resulting in weight loss. ESG is an outpatient procedure, and patients can typically go home the same day.
Compared to traditional bariatric surgeries such as gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy, ESG is less invasive and has a lower risk of complications. A systematic review and meta-analysis assessing the ASGE PIVI thresholds for adopting endoscopic bariatric therapies showed that ESG resulted in a mean excess weight loss of 15.9% at 12 months, which was statistically significant and met the PIVI threshold for clinical success. Moreover, a study by Sharaiha et al. found that ESG significantly reduces body mass index (BMI) and metabolic complications in obese patients, including type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol.
Who is it recommended for? Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty
ESG is typically recommended for patients with a BMI of 30 to 40 who have not achieved success with diet and exercise alone. Eligibility criteria for ESG may also include a history of weight-related health problems, such as sleep apnea or joint pain. ESG is not suitable for patients who have had prior gastrointestinal surgeries, have a history of bleeding disorders, or are pregnant.
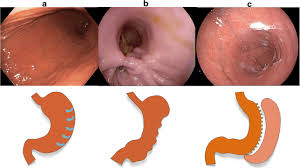
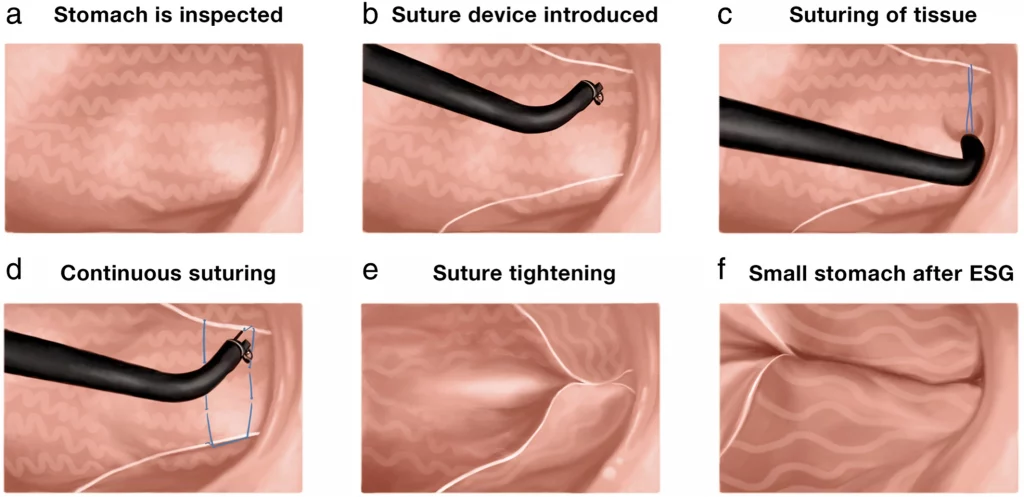
During the ESG procedure, patients are sedated and a flexible endoscope is inserted through the mouth into the stomach. The endoscope is then used to place sutures along the stomach’s greater curvature, creating a sleeve-like shape. The procedure takes approximately 60-90 minutes to complete.
Overall, ESG is a safe and effective weight loss option for eligible patients. Like any medical procedure, it does come with potential risks and complications. It is important to discuss the risks and benefits of ESG with a healthcare provider[4] to determine if it is the right option for you.
Preparing for ESG
Preparing for Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG) involves several steps:
Include consultation with a healthcare provider, pre-procedure requirements, and dietary and lifestyle changes. These steps are essential for ensuring the procedure’s success and minimizing potential risks and complications.
Consultation with a healthcare provider is the first step in preparing for ESG. During this consultation, patients will discuss their weight loss goals and medical history with their healthcare provider.[5] The healthcare provider will also assess the patient’s eligibility for ESG and discuss the procedure’s risks and benefits. In addition, patients will receive instructions on how to prepare for the procedure and any necessary pre-procedure testing.
Pre-procedure requirements for ESG may include fasting for a certain period before the procedure, stopping certain medications, and avoiding smoking. Patients may also need to undergo tests, such as blood work or imaging studies, before the procedure.
Dietary and lifestyle changes with endoscopic sleeve
Dietary and lifestyle changes are also essential for preparing for ESG. Patients will need to follow a specific diet before the procedure, which may include a low-calorie diet or a liquid diet. These diets help to reduce the size of the liver and make the procedure safer and more comfortable. Patients will also need to make long-term dietary changes to support weight loss after the procedure.
In addition to dietary changes, patients will need to make lifestyle changes to support weight loss after ESG. This may include increasing physical activity and reducing sedentary behavior. Patients will also need to attend follow-up appointments and make adjustments to their diet and exercise routine based on their healthcare provider’s recommendations.
In summary, preparing for ESG involves several steps, including consultation with a healthcare provider, pre-procedure requirements, and dietary and lifestyle changes. These steps is essential for ensuring the procedure’s success and achieving long-term weight loss.
The ESG Procedure
Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG) is a minimally invasive weight loss procedure that involves using an endoscope to reduce the size of the stomach. ESG typically takes 60-90 minutes[6] to complete and is performed under sedation. The following section will provide a detailed description of what to expect during the ESG procedure, including the duration of the procedure and anesthesia.
During the ESG procedure, patients lie on their back while the endoscope is inserted through their mouth into the stomach. The endoscope is equipped with a suturing device that is used to place sutures along the stomach’s greater curvature, creating a sleeve-like shape. The sutures help to reduce the size of the stomach and create a feeling of fullness, resulting in weight loss. The procedure is performed entirely through the mouth, and there are no incisions or scars.
The duration of the ESG procedure is typically 60-90 minutes, depending on the complexity of the patient’s case. Patients are sedated during the procedure and are generally unaware of what is happening. After the procedure is complete, patients are taken to a recovery area, where they are monitored until the effects of the sedation wear off.
Anesthesia during the endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty
Anesthesia during the ESG procedure is typically provided by a board-certified anesthesiologist.[7] The type of anesthesia used may vary depending on the patient’s medical history and the healthcare provider’s recommendations. Generally, patients are given a combination of sedatives and pain relievers to ensure their comfort during the procedure. The anesthesia used during ESG is typically safe, and the risk of complications is low.
ESG procedure is a safe and effective weight loss option for eligible patients. However, like any medical procedure, it does come with potential risks and complications. It is essential to discuss the risks and benefits of ESG with a healthcare provider to determine if it is the right option for you.
Recovery from ESG
Recovery from Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG) is relatively for most patients
Patients resume their normal activities within a few days. However, it is essential to follow post-procedure guidelines to ensure a smooth recovery and reduce the risk of complications.[8]
After ESG, patients will be taken to a recovery area where they will be monitored until the effects of the sedation wear off. Patients may experience some discomfort, bloating, or nausea immediately after the procedure, but these symptoms generally subside within a few hours. Patients are typically discharged from the hospital on the same day as the procedure.
Dietary & lifestyle changes after endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty
Patients will need to follow a specific diet for several weeks after the procedure. This diet may include a liquid or soft food diet for the first few days, followed by a gradual transition to solid foods. Patients will also need to avoid certain foods, such as spicy or acidic foods, for a few weeks after the procedure.
In addition to dietary changes, patients will need to make lifestyle changes to support weight loss after ESG. This may include increasing physical activity, reducing sedentary behavior, and attending follow-up appointments with their healthcare provider.
Potential risks and complications with endoscopic
ESG is generally well-tolerated, and most patients experience few complications. However, like any medical procedure, there are potential risks and complications, including bleeding, infection, or injury to the stomach or other organs. Patients should contact their healthcare provider immediately if they experience severe or persistent abdominal pain, fever, or other symptoms after the procedure.
Recovery from ESG involves following post-procedure guidelines, including dietary and lifestyle changes, to support weight loss and reduce the risk of complications. Patients should discuss post-procedure guidelines with their healthcare provider to ensure a smooth recovery and achieve long-term weight loss.
Conclusion
Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG) is a minimally invasive weight loss procedure that can be an effective option for eligible patients.[9] ESG involves using an endoscope to reduce the size of the stomach, which creates a feeling of fullness and helps to support weight loss. While ESG is generally safe and well-tolerated, it is essential to discuss the risks and benefits with a healthcare provider to determine if it is the right option for you.
Preparing for ESG involves several steps:
Including consultation with a healthcare provider, pre-procedure requirements, and dietary and lifestyle changes. Patients will need to follow specific post-procedure guidelines to ensure a smooth recovery and support long-term weight loss. Recovery from ESG is relatively quick, and most patients can resume their normal activities within a few days.
ESG is just one of many weight loss options available, and it is essential to discuss all options with a healthcare provider to determine the best approach for you. However, for eligible patients, ESG can be an effective and minimally invasive option for achieving long-term weight loss.
In conclusion, ESG is a safe and effective weight loss procedure that can help eligible patients achieve their weight loss goals. It is essential to discuss all options with a healthcare provider and follow pre- and post-procedure guidelines to ensure a successful outcome.[10]
References
- Sharaiha RZ, Kumta NA, Saumoy M, et al. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty significantly reduces body mass index and metabolic complications in obese patients. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15(4):504-510.e2. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28017845/
- ASGE Bariatric Endoscopy Task Force; Abu Dayyeh BK, Kumar N, Edmundowicz SA, et al. ASGE Bariatric Endoscopy Task Force systematic review and meta-analysis assessing the ASGE PIVI thresholds for adopting endoscopic bariatric therapies. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;82(3):425-438.e5.
- Sharaiha RZ, Kedia P, Kumta N, et al. Initial experience with endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty: technical success and reproducibility in the bariatric population. Endoscopy. 2015;47(2):164-166.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25380510/
- Arrese M, Barría C, Sánchez P, et al. Efficacy of endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) for weight loss in obese patients. Obes Surg. 2017;27(9):2250-2258.
- Kumar N, Sullivan S, Thompson CC. The role of endoscopic therapy in obesity management: intragastric balloons and beyond. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2017;33(4):294-301. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28740414/
- ASGE Bariatric Endoscopy Task Force; Abu Dayyeh BK, Kumar N, Edmundowicz SA, et al. ASGE Bariatric Endoscopy Task Force systematic review and meta-analysis assessing the ASGE PIVI thresholds for adopting endoscopic bariatric therapies. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;82(3):425-438.e5. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26232362/
- Sharaiha RZ, Kumta NA, Saumoy M, et al. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty significantly reduces body mass index and metabolic complications in obese patients. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15(4):504-510.e2.
- Genco A, Soricelli E, Casella G, et al. Gastroesophageal reflux disease and Barrett’s esophagus after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: a possible, underestimated long-term complication. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2017;13(4):568-574.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28089434/
- Sharaiha RZ, Kedia P, Kumta N, et al. Initial experience with endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty: technical success and reproducibility in the bariatric population. Endoscopy. 2015;47(2):164-166.
- Lopez-Nava G, Galvão MP, Bautista-Castaño I, et al. Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty: how I do it?. Obes Surg. 2015;25(8):1534-1538.